Shear and Threaded Stud Grades
- General Overview
- Tips and Tricks
- Related Tools
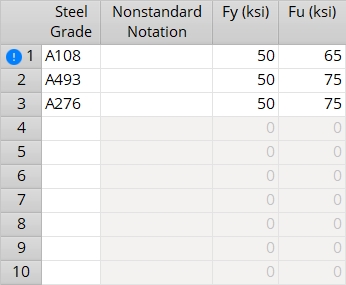
- Warning: Changing any steel grade definition (for example, changing line 3) assigns the new definition to all materials that had been assigned the previous definition. Since a steel grade is assigned to a material by its line number (index), this means that if you switch line 3 with line 4, the steel grades of existing materials using those definitions will also be switched.
Available Settings by Design Method
| Screen | Columns | When Shown |
| ASD/LRFD/CISC | Line number, Steel Grade, Nonstandard Notation, Fy, Fu | shown when an ASD, LRFD, or CISC Connection design method is selected. |
| AS4100 | Line number, Steel Grade, Nonstandard Notation, Fy, Fu, Minimum Thickness, Maximum Thickness | shown when AS 4100 is the Connection design method. |
| Eurocode | Line number, Steel Grade, Nonstandard Notation, Fy, Fu, Minimum Thickness, Maximum Thickness, Correlation Factor | shown when EUROCODE3 or EUROCODE3 UK is the Connection design method. |
Settings
Line number: The index number (a positive integer) of the steel grade -- see the warning. The steel grade entered to line 1 on this window is assigned as the default Steel grade to the first shear stud or threaded stud that is added using Add Material or Add Miscellaneous Member after you first start Modeling.
To move a line up or down in priority: Left-click to select the line and hold down the left-mouse button, then drag the line up or down.
Steel Grade: Any text string (up to 29 characters) to denote the name of the steel grade (e.g., A108, A493, Peter, Joe, whatever name you want). Steel grades entered here are selectable  )
)
Nonstandard Notation: Any text string (up to 29 characters) to denote that a particular steel grade is not the standard steel grade.
| For submaterials: A callout is generated next to that material's submaterial piecemark callout on the member detail when Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Piecemarking > Member and Material Piecemarking > Submaterial > |
Minimum Thickness & Maximum Thickness (AS4100 and Eurocode): These columns let you assign Fy (yield strength) and Fu (ultimate strength) values to a steel grade based on the diameter of the stud material.
Fy: The yield strength of the steel grade. If you are using imperial dimensioning, yield strength is measured in kips/sq. inch (ksi). If you are using metric dimensioning, yield strength is measured in megapascals (MPa). Since connection design does not evaluate Fy and Fu values for shear studs or threaded studs, this value is for your reference only.
Fu: The ultimate strength of the steel grade. If you are using imperial dimensioning, ultimate strength is measured in kips/sq. inch (ksi). If you are using metric dimensioning, ultimate strength is in megapascals (MPa). Since connection design does not evaluate Fy and Fu values for shear studs or threaded studs, this value is for your reference only.
Correlation Factor (Eurocode): The appropriate correlation factor (ß w ) taken from Table 4.1 in BS EN 1993-1-8: 2005, Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures. The factor is used in calculations for fillet welds.
|
|
OK (or the Enter key) closes this screen and applies the settings.
Cancel (or the Esc key) closes this screen without saving any changes.
Reset undoes all changes made to this screen since you first opened it. The screen remains open.
- Steel grade (to apply grades on this screen to shear studs or threaded studs)
- Material steel grade (Status Display)
 or
or 